Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®) is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that is given as a once-weekly subcutaneous injection for “chronic weight management” in specified subgroups of patients (see FDA indications below).
Optional to read: Semaglutide was approved by the FDA in 2021 and was the first weight-loss medication to be approved since 2014.
On this page, we will provide basic information about this medication. Links to other articles on this website with more advanced information and tips related to this medication and related topics are provided below, under Related Pages.
FDA indications
According to the Prescribing Information, the wording of the FDA indications for semaglutide injection (Wegovy®) is as follows (the emphasis below in red has been added by us):
“WEGOVY is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist indicated in combination with a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity:
• to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke) in adults with established cardiovascular disease and either obesity or overweight.
• to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
o Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity
o Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition”
For more on the use of semaglutide injection (Wegovy®) to treat obesity and overweight, please see the following article on this website:
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®) for weight loss in obesity and overweight
Mechanism of Action/ Pharmacodynamics
Semaglutide belongs to a group of medications called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists. GLP-1 is involved in the regulation of appetite and food intake.
For more on what GLP-1 is and an overview of other GLP-1 agonists, please see the following article on this website:
A simple primer on what GLP-1 agonists are
Relatively common side effects
In clinical trials, side effects that occurred on semaglutide injection (Wegovy®) with at least a 2% drug-placebo difference were:
1. Gastrointestinal:
All kinds of gastrointestinal side effects can occur (in decreasing order of incidence)—Nausea (28%), vomiting (18%), diarrhea (14%, close to twice as often on medication as on placebo), constipation (13%), abdominal pain (10%), dyspepsia (indigestion; 6%), eructation (belching; 6%), gastritis (2%).
2. Fatigue (6%)
3. Dizziness (4%)
4. Hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes (4%)
5. Hair loss (3%)
For more about the relatively common side effects of semaglutide injection (Wegovy®), please see the following article on this website:
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®): Side effects
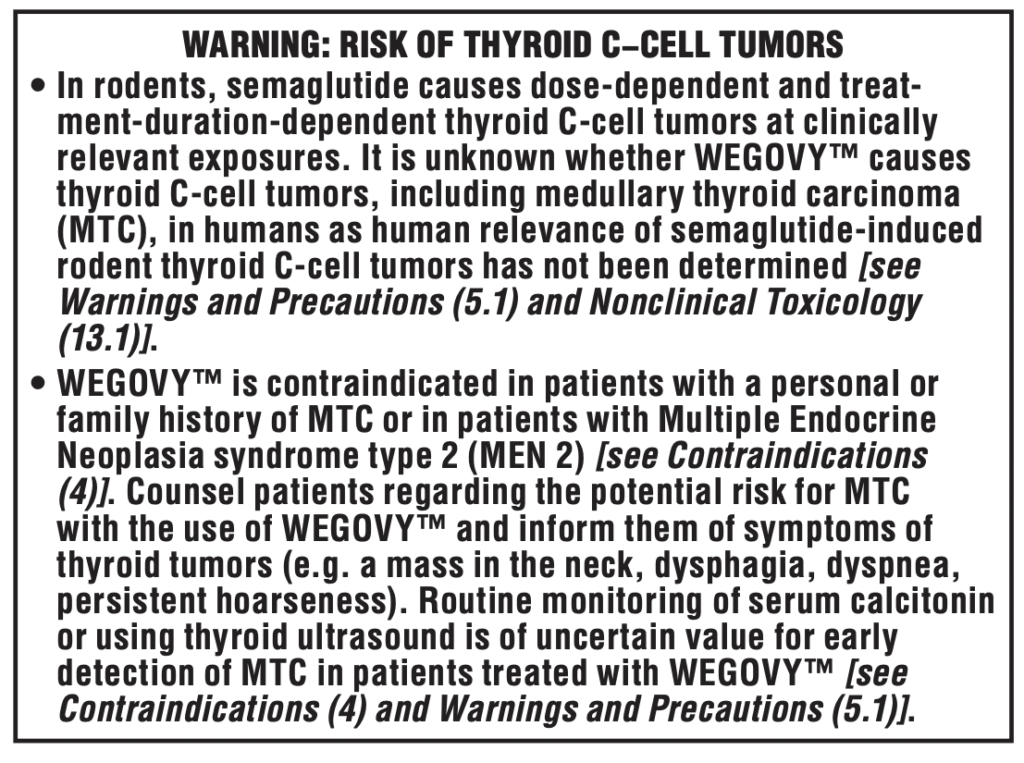
Boxed warning
Other potential serious side effects (Warnings and Precautions)
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy™) comes with the following nine “Warnings and Precautions” , which are worded exactly as in the official Prescribing Information:
1. Thyroid C-cell tumors (boxed warning)
2. Acute pancreatitis
3. Acute gallbladder disease
4. Hypoglycemia
5. Acute kidney injury
6. Hypersensitivity
7. Diabetic retinopathy complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
8. Heart rate increase
9. Suicidal behavior and ideation
10. Delayed gastric emptying
For important points on these ten “Warnings and Precautions” about semaglutide injection (Wegovy™) and what we need to do about them, please see the following article on this website:
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®): Serious side effects, warnings, and contraindications
Dosage and Administration
The medication dose must be increased gradually over 16 to 20 weeks to 2.4 mg once weekly to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Dosage forms and strengths
Wegovy™ is available as a single-use, prefilled syringe in 5 different strengths: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, and 2.4 mg.
Optional to read: In contrast, Ozempic® is available as prefilled syringes containing 2 mg, 4 mg, or 8 mg of semaglutide. But, these syringes are not for single use. They can be used to deliver specific doses of semaglutide until the medication in that syringe is used up, as follows:
– The syringe containing 2 mg can deliver either 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg at a time
– The syringe containing 4 mg delivers 1 mg at a time
– The syringe containing 8 mg delivers 2 mg at a time.
Important! This page does not provide all the information needed to prescribe this medication. Please refer to the full Prescribing Information (see link below) before prescribing this medication.
Related Pages
GLP-1 agonists
A simple primer on what GLP-1 agonists are
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®) for weight loss in obesity and overweight
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®): Side effects
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®): Serious side effects, warnings, and contraindications
Semaglutide injection (Wegovy®): Basic information
Metabolic side effects: General
Do adolescents have more metabolic side effects with second-generation antipsychotics?
Does weight gain with second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics plateau after the first few months?
How long does antipsychotic-induced hyperglycemia take to resolve?
Resolution of hyperglycemia after switching to aripiprazole
Should we prescribe medications for weight loss?
Why it is important to treat obesity
Medications for the treatment of obesity: Overview
Metabolic side effects: Monitoring
Monitoring for metabolic side effects in patients on a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic
Monitoring for metabolic side effects in children and adolescents on a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic
Metabolic side effects: Metformin
Metformin to prevent or treat metabolic adverse effects due to antipsychotics
Who is more likely to benefit from metformin for the management of metabolic adverse effects?
Metformin for antipsychotic-induced weight gain in children and adolescents?
Potential adverse effects of metformin
Tips on prescribing metformin
Metformin AND topiramate for metabolic adverse effects?
Metabolic side effects: Topiramate
Can we use topiramate to treat medication-induced weight gain?
Metformin AND topiramate for metabolic adverse effects?
Metabolic side effects: Naltrexone/ bupropion
Naltrexone and bupropion (Contrave®): Basic Information
A generic alternative to naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave®)?
Metabolic side effects: Miscellaneous
Phentermine-topiramate combination (Qsymia) for weight loss
Orlistat (Xenical®): Basic Information
Phentermine (Adipex-P®, Lomaira™): Basic information
Can melatonin increase blood sugar?
HTR2C polymorphisms and medication-induced weight gain
Melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) and weight gain
References
Wegovy® Prescribing Information
Taha MB, Yahya T, Satish P, Laird R, Agatston AS, Cainzos-Achirica M, Patel KV, Nasir K. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: A Medication for Obesity Management. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2022 May 28. doi: 10.1007/s11883-022-01041-7. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35624390.
Copyright © 2022 to 2025, Simple and Practical Medical Education, LLC. All rights reserved. The content on this website may not be reproduced in any form without express written permission.
Disclaimer: The material on this website is provided as general education for medical professionals. It is not intended for patients or other laypersons, nor is it a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Patients must always consult a qualified healthcare professional regarding their diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare professionals should always check this website for the most up-to-date information.
Leave a Reply